Chapter 12 : Burn EmergenciesDefined:The skin is the body’s largest organ. A burn is an injury to this organ, the skin. Burn treatments vary based on the severity of the injury. Causes:
Signs and Symptoms:
Common Emergency Example(s):
First Degree Burn (Superficial):A first degree burn affects only the uppermost or outer layer of the skin. This burn causes mild redness, swelling and pain. Second Degree Burn (Partial Thickness):A second degree, or partial thickness, burn affects both the upper layer of the skin and the skin underneath it. Some specific symptoms for this burn include: redness, swelling, pain and blistering. Third Degree Burn (Full Thickness):A third degree, or full thickness, burn is the most severe and destroys the deep layers of the skin. This can lead to numb skin and white or blackened skin. DO NOT:
First Aid Actions / Treatment:
|
|
The skin is the body’s largest organ. A burn is an injury to this organ, the skin. Burn treatments vary based on the severity of the injury.
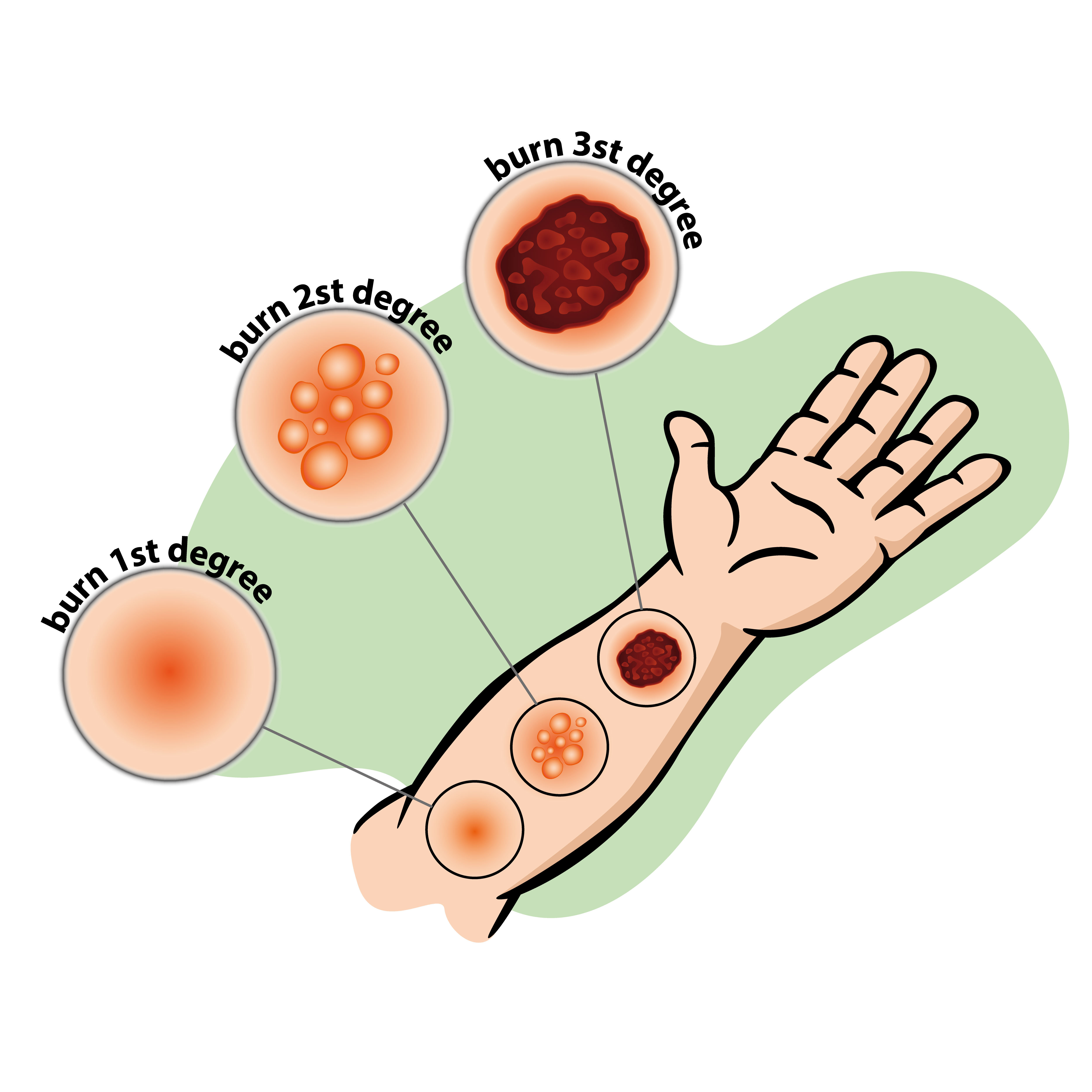
A first degree burn affects only the uppermost or outer layer of the skin. This burn causes mild redness, swelling and pain.
A second degree, or partial thickness, burn affects both the upper layer of the skin and the skin underneath it. Some specific symptoms for this burn include: redness, swelling, pain and blistering.
A third degree, or full thickness, burn is the most severe and destroys the deep layers of the skin. This can lead to numb skin and white or blackened skin.
DO NOT: